– Phase 1b data for glesatinib shows clinical activity with durable confirmed partial responses and tumor regressions in selected NSCLC patients; ongoing Phase 2 trial to optimize exposures and clinical benefit with updated formulation
– Initial sitravatinib Phase 1b data presented at ASCO demonstrate early signs of clinical activity, including a confirmed partial response
– Phase 2 trial for mocetinostat in combination with durvalumab initiated and enrolling patients
SAN DIEGO, CA, USA I June 5, 2016 I Mirati Therapeutics, Inc. (MRTX) today provided an update on three current ongoing clinical programs in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other solid tumors.
“We are making significant progress in the development of our pipeline as our ongoing clinical programs are showing meaningful results,” said Charles M. Baum, M.D., Ph.D., president and CEO. “We have confirmed responses including sustained activity in our glesatinib program, and encouraging signs of early efficacy from sitravatinib. These data demonstrate our ability to advance our targeted oncology drug candidates through our differentiated development approach. Today we also announced the start of our mocetinostat combination trial, our first in immuno-oncology. We are excited about the potential to deliver meaningful data points on all three of our clinical programs in 2016 and into 2017.”
Glesatinib Program Update
Glesatinib Phase 1b Trial
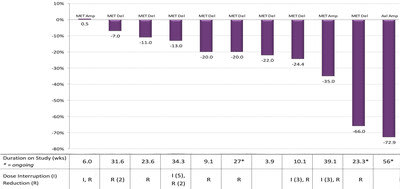
As of May 20, 2016, 28 patients with MET and AXL alterations were enrolled in the Phase 1b trial across multiple tumor types, including 22 NSCLC patients. A majority of these patients were heavily pretreated with multiple lines of prior therapy including radiation and/or surgery. Eleven of the NSCLC patients had genetic driver alterations comparable to the criteria in our ongoing Phase 2 trial, including two NSCLC patients with MET amplifications, eight NSCLC patients with MET exon14 deletion mutations, and one NSCLC patient with AXL amplification.
The results demonstrate tumor regression in the majority of patients including confirmed responses to glesatinib:
- 3 of 11 NSCLC patients had partial responses (PRs) confirmed per RECIST, including patients with a MET amplification, MET exon14 deletion mutation and AXL amplification
- Patients with confirmed responses were on study for 39 weeks, 23 weeks and 56 weeks, with the 23 and 56 week patients continuing on study
- Tumor regression was seen in 10 of the 11 patients, three of which had confirmed PRs
The chart included shows the best response for these 11 patients by their specific alteration as of May 20, 2016. For full resolution image click here.
During the course of the Phase 1b trial, the majority of the NSCLC patients (nine of 11) experienced dose reductions and/or dose interruptions. These events may have resulted in decreased exposure levels needed to fully inhibit MET throughout the treatment cycle.
Of the nine patients whose doses were reduced during the trial, two had a second dose reduction; four patients had dose interruptions and three had multiple dose interruptions while on study. Of the patients no longer on trial, five discontinued due to disease progression, two were related to AEs (one incidence of nausea and vomiting and one diarrhea) and one patient withdrew consent.
The dose reductions and interruptions were due primarily to episodes of diarrhea, potentially associated with the original miglyol (an oil-based excipient similar to castor oil) formulation of glesatinib administered during the trial, which may have contributed to or exacerbated diarrhea.
A new formulation of glesatinib is being implemented in the ongoing Phase 2 trial to reduce dose reductions and interruptions and to optimize exposure levels throughout the treatment regimen. The new spray-dried dispersion (SDD) formulation of glesatinib was evaluated in a dose escalation arm of the Phase 1b study and a recommended Phase 2 dose of 750mg BID was established.
The patient with a MET exon14 deletion and confirmed PR has shown significant tumor regression as well as improved tolerability after moving to the new formulation at a dose of 500mg BID. Following two full cycles of treatment with the new formulation, the patient experienced a deepening PR, from 45% to 66%, and remains on study.
Data from the Phase 1b trial has shown the SDD formulation to have several advantages including: (i) fewer tablets per dose; (ii) better relative bioavailability than the original formulation supporting full target inhibition; (iii) improved tolerability; and (iv) manufacturing advantages.
“We believe that the combination of improved tolerability and bioavailability of the new formulation will allow patients to remain on the intended dose, extend the duration of treatment and possibly increase response rates,” continued Baum. “Because development of the new formulation was already in process for integration into the Phase 2 trial for use commercially, the change has already been discussed with the FDA and is moving forward.”
Glesatinib Phase 2 Trial
The Phase 2 trial for glesatinib continues in NSCLC patients with MET genetic alterations of interest who were previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and those who may also have had prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor. Enrollment is ongoing and the new formulation is being introduced this month. Patients who started on the original formulation will be transitioned to the new formulation. An interim update on response rates in patients from the Phase 2 study on the new formulation will be provided once a meaningful number of patients have been treated and are evaluable.
Patient screening continues to increase and 55 clinical sites are active globally, with approximately 130 sites planned in total. In addition to clinical screening at study sites, unique patient finding and outreach collaborations with Foundation Medicine and Guardant Health have identified more than 160 additional patients with MET amplification and exon14 deletion in the first three months. Our experience confirms the prevalence of these patient populations and the value of these collaborations, which expand our clinical reach beyond our dedicated trial sites.
The Company is exploring development of glesatinib for patients with AXL genetic alterations based upon the NSCLC AXL amplification patient who has now had a durable confirmed response to glesatinib for over a year and continues on trial.
Sitravatinib Program Update
Initial data from the Phase 1b trial of sitravatinib show early signs of clinical activity, including a confirmed PR in a Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) patient, as well as durable tumor regressions in multiple other tumor types, including NSCLC patients with RET mutations. The Phase 1b trial in sitravatinib continues to enroll patients with RET, CHR4q12, CBL, TRK and DDR genetic alterations in NSCLC and other solid tumors at sites in the U.S. and Korea.
A poster entitled, “A first in human Phase 1 study of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor MGCD516 in patients with advanced solid tumors” presented at the 2016 ASCO Annual Meeting includes this initial clinical data, which further demonstrates the safety and tolerability of sitravatinib. The poster can be found at www.mirati.com.
The Phase 1b trial includes multiple cohorts to explore the safety and efficacy of sitravatinib in genetically selected patients with NSCLC, as well as cohorts in certain solid tumors where the profile of sitravatinib may provide clinical benefit. Based upon our experience to date, sitravatinib is generally well tolerated at the recommended Phase 2 dose of 150mg, administered once daily (QD).
An additional update on this trial is expected by the end of the year, when a greater number of patients have been enrolled.
Mocetinostat Program Update
The Company has initiated a trial for the combination study of mocetinostat, an HDAC (histone deacetylase) inhibitor, with the AstraZeneca/MedImmune anti-PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitor, durvalumab, in patients with NSCLC.
This trial is exploring the potential of mocetinostat to enhance the effectiveness of checkpoint inhibitors in NSCLC. The dual effect of Class I HDACs on tumor cells, as well as on immune cells, may enhance the effect of checkpoint inhibitors in all indications where checkpoint inhibitors have demonstrated efficacy.
The Company plans to provide an update on this Phase 2 trial as progress continues, with the potential to see initial signals of activity by early 2017.
About Mirati
Mirati Therapeutics develops molecularly targeted therapies intended to treat cancer by combining the three most important factors in oncology drug development: 1) researching and developing drug candidates that target genetic and epigenetic drivers of cancer as single agents and in combination, including combination with immune therapy, 2) designing creative and agile clinical development strategies that select for patients whose tumors are dependent on specific driver alterations, and 3) leveraging a highly accomplished oncology precision medicine leadership team. The Mirati team uses a blueprint proven by their prior work for developing potential breakthrough cancer therapies with accelerated development paths to improve outcomes for patients. Mirati is advancing three drug candidates through clinical development for multiple oncology indications. More information is available at www.mirati.com.
About Glesatinib (MGCD265)
Glesatinib (MGCD265) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that potently and selectively targets tumors in patients with driver alterations in MET (mutations and gene amplification) and Axl (rearrangements and gene amplification) that occur in approximately 8% of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Genetic alterations in these targets have been implicated as drivers of tumor growth and disease progression in NSCLC and other solid tumors. Glesatinib is being evaluated in a Phase 2 trial in NSCLC patients with MET genetic alterations to confirm and extend the data that supports the clinical benefit of glesatinib in patients with driver mutations in MET. Mirati retains worldwide rights to glesatinib.
About Sitravatinib (MGCD516)
Sitravatinib (MGCD516) is being evaluated in a Phase 1b dose expansion cohort in selected patients with specific genetic alterations that are drivers of tumor growth, with an initial focus on NSCLC and in other solid tumors where sitravatinib may confer a benefit. Sitravatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor with demonstrated potent inhibition of a closely related spectrum of tyrosine kinases, including RET, CBL, CHR4q12, DDR and Trk, which are key regulators of signaling pathways that lead to cell growth, survival and tumor progression. Mirati retains worldwide rights to sitravatinib.
About Mocetinostat (MGCD103)
Mocetinostat (MGCD103) is an orally-bioavailable, spectrum-selective Class I & IV HDAC inhibitor currently being studied in a Phase 2 trial as a combination therapy with durvalumab, targeting the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) pathway, which has been implicated in advanced lung cancers. In preclinical models, mocetinostat with durvalumab demonstrated significant reduction in tumor volume compared to either agent alone.
About Durvalumab
Durvalumab is an investigational human monoclonal antibody directed against programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1). PD-L1 expression enables tumors to evade detection from the immune system through binding to PD-1 on cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Durvalumab blocks PD-L1 interaction with both PD-1 and CD80 on T cells, countering the tumour’s immune-evading tactics. Durvalumab is being developed alongside other immunotherapies to activate the patient’s immune system to attack the cancer. Durvalumab is being investigated in an extensive clinical trial programme, as monotherapy or in combination with tremelimumab, in NSCLC, bladder, head and neck, gastric, pancreatic, HCC and blood cancers. In 2015, durvalumab received Fast Track Designation for the treatment of patients with PD-L1–positive metastatic SCCHN, and in 2016, durvalumab was granted Breakthrough Designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a potential treatment for metastatic urothelial bladder cancer.
SOURCE: Mirati Therapeutics
Post Views: 203
– Phase 1b data for glesatinib shows clinical activity with durable confirmed partial responses and tumor regressions in selected NSCLC patients; ongoing Phase 2 trial to optimize exposures and clinical benefit with updated formulation
– Initial sitravatinib Phase 1b data presented at ASCO demonstrate early signs of clinical activity, including a confirmed partial response
– Phase 2 trial for mocetinostat in combination with durvalumab initiated and enrolling patients
SAN DIEGO, CA, USA I June 5, 2016 I Mirati Therapeutics, Inc. (MRTX) today provided an update on three current ongoing clinical programs in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other solid tumors.
“We are making significant progress in the development of our pipeline as our ongoing clinical programs are showing meaningful results,” said Charles M. Baum, M.D., Ph.D., president and CEO. “We have confirmed responses including sustained activity in our glesatinib program, and encouraging signs of early efficacy from sitravatinib. These data demonstrate our ability to advance our targeted oncology drug candidates through our differentiated development approach. Today we also announced the start of our mocetinostat combination trial, our first in immuno-oncology. We are excited about the potential to deliver meaningful data points on all three of our clinical programs in 2016 and into 2017.”
Glesatinib Program Update
Glesatinib Phase 1b Trial
As of May 20, 2016, 28 patients with MET and AXL alterations were enrolled in the Phase 1b trial across multiple tumor types, including 22 NSCLC patients. A majority of these patients were heavily pretreated with multiple lines of prior therapy including radiation and/or surgery. Eleven of the NSCLC patients had genetic driver alterations comparable to the criteria in our ongoing Phase 2 trial, including two NSCLC patients with MET amplifications, eight NSCLC patients with MET exon14 deletion mutations, and one NSCLC patient with AXL amplification.
The results demonstrate tumor regression in the majority of patients including confirmed responses to glesatinib:
- 3 of 11 NSCLC patients had partial responses (PRs) confirmed per RECIST, including patients with a MET amplification, MET exon14 deletion mutation and AXL amplification
- Patients with confirmed responses were on study for 39 weeks, 23 weeks and 56 weeks, with the 23 and 56 week patients continuing on study
- Tumor regression was seen in 10 of the 11 patients, three of which had confirmed PRs
The chart included shows the best response for these 11 patients by their specific alteration as of May 20, 2016. For full resolution image click here.
During the course of the Phase 1b trial, the majority of the NSCLC patients (nine of 11) experienced dose reductions and/or dose interruptions. These events may have resulted in decreased exposure levels needed to fully inhibit MET throughout the treatment cycle.
Of the nine patients whose doses were reduced during the trial, two had a second dose reduction; four patients had dose interruptions and three had multiple dose interruptions while on study. Of the patients no longer on trial, five discontinued due to disease progression, two were related to AEs (one incidence of nausea and vomiting and one diarrhea) and one patient withdrew consent.
The dose reductions and interruptions were due primarily to episodes of diarrhea, potentially associated with the original miglyol (an oil-based excipient similar to castor oil) formulation of glesatinib administered during the trial, which may have contributed to or exacerbated diarrhea.
A new formulation of glesatinib is being implemented in the ongoing Phase 2 trial to reduce dose reductions and interruptions and to optimize exposure levels throughout the treatment regimen. The new spray-dried dispersion (SDD) formulation of glesatinib was evaluated in a dose escalation arm of the Phase 1b study and a recommended Phase 2 dose of 750mg BID was established.
The patient with a MET exon14 deletion and confirmed PR has shown significant tumor regression as well as improved tolerability after moving to the new formulation at a dose of 500mg BID. Following two full cycles of treatment with the new formulation, the patient experienced a deepening PR, from 45% to 66%, and remains on study.
Data from the Phase 1b trial has shown the SDD formulation to have several advantages including: (i) fewer tablets per dose; (ii) better relative bioavailability than the original formulation supporting full target inhibition; (iii) improved tolerability; and (iv) manufacturing advantages.
“We believe that the combination of improved tolerability and bioavailability of the new formulation will allow patients to remain on the intended dose, extend the duration of treatment and possibly increase response rates,” continued Baum. “Because development of the new formulation was already in process for integration into the Phase 2 trial for use commercially, the change has already been discussed with the FDA and is moving forward.”
Glesatinib Phase 2 Trial
The Phase 2 trial for glesatinib continues in NSCLC patients with MET genetic alterations of interest who were previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and those who may also have had prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor. Enrollment is ongoing and the new formulation is being introduced this month. Patients who started on the original formulation will be transitioned to the new formulation. An interim update on response rates in patients from the Phase 2 study on the new formulation will be provided once a meaningful number of patients have been treated and are evaluable.
Patient screening continues to increase and 55 clinical sites are active globally, with approximately 130 sites planned in total. In addition to clinical screening at study sites, unique patient finding and outreach collaborations with Foundation Medicine and Guardant Health have identified more than 160 additional patients with MET amplification and exon14 deletion in the first three months. Our experience confirms the prevalence of these patient populations and the value of these collaborations, which expand our clinical reach beyond our dedicated trial sites.
The Company is exploring development of glesatinib for patients with AXL genetic alterations based upon the NSCLC AXL amplification patient who has now had a durable confirmed response to glesatinib for over a year and continues on trial.
Sitravatinib Program Update
Initial data from the Phase 1b trial of sitravatinib show early signs of clinical activity, including a confirmed PR in a Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) patient, as well as durable tumor regressions in multiple other tumor types, including NSCLC patients with RET mutations. The Phase 1b trial in sitravatinib continues to enroll patients with RET, CHR4q12, CBL, TRK and DDR genetic alterations in NSCLC and other solid tumors at sites in the U.S. and Korea.
A poster entitled, “A first in human Phase 1 study of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor MGCD516 in patients with advanced solid tumors” presented at the 2016 ASCO Annual Meeting includes this initial clinical data, which further demonstrates the safety and tolerability of sitravatinib. The poster can be found at www.mirati.com.
The Phase 1b trial includes multiple cohorts to explore the safety and efficacy of sitravatinib in genetically selected patients with NSCLC, as well as cohorts in certain solid tumors where the profile of sitravatinib may provide clinical benefit. Based upon our experience to date, sitravatinib is generally well tolerated at the recommended Phase 2 dose of 150mg, administered once daily (QD).
An additional update on this trial is expected by the end of the year, when a greater number of patients have been enrolled.
Mocetinostat Program Update
The Company has initiated a trial for the combination study of mocetinostat, an HDAC (histone deacetylase) inhibitor, with the AstraZeneca/MedImmune anti-PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitor, durvalumab, in patients with NSCLC.
This trial is exploring the potential of mocetinostat to enhance the effectiveness of checkpoint inhibitors in NSCLC. The dual effect of Class I HDACs on tumor cells, as well as on immune cells, may enhance the effect of checkpoint inhibitors in all indications where checkpoint inhibitors have demonstrated efficacy.
The Company plans to provide an update on this Phase 2 trial as progress continues, with the potential to see initial signals of activity by early 2017.
About Mirati
Mirati Therapeutics develops molecularly targeted therapies intended to treat cancer by combining the three most important factors in oncology drug development: 1) researching and developing drug candidates that target genetic and epigenetic drivers of cancer as single agents and in combination, including combination with immune therapy, 2) designing creative and agile clinical development strategies that select for patients whose tumors are dependent on specific driver alterations, and 3) leveraging a highly accomplished oncology precision medicine leadership team. The Mirati team uses a blueprint proven by their prior work for developing potential breakthrough cancer therapies with accelerated development paths to improve outcomes for patients. Mirati is advancing three drug candidates through clinical development for multiple oncology indications. More information is available at www.mirati.com.
About Glesatinib (MGCD265)
Glesatinib (MGCD265) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that potently and selectively targets tumors in patients with driver alterations in MET (mutations and gene amplification) and Axl (rearrangements and gene amplification) that occur in approximately 8% of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Genetic alterations in these targets have been implicated as drivers of tumor growth and disease progression in NSCLC and other solid tumors. Glesatinib is being evaluated in a Phase 2 trial in NSCLC patients with MET genetic alterations to confirm and extend the data that supports the clinical benefit of glesatinib in patients with driver mutations in MET. Mirati retains worldwide rights to glesatinib.
About Sitravatinib (MGCD516)
Sitravatinib (MGCD516) is being evaluated in a Phase 1b dose expansion cohort in selected patients with specific genetic alterations that are drivers of tumor growth, with an initial focus on NSCLC and in other solid tumors where sitravatinib may confer a benefit. Sitravatinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor with demonstrated potent inhibition of a closely related spectrum of tyrosine kinases, including RET, CBL, CHR4q12, DDR and Trk, which are key regulators of signaling pathways that lead to cell growth, survival and tumor progression. Mirati retains worldwide rights to sitravatinib.
About Mocetinostat (MGCD103)
Mocetinostat (MGCD103) is an orally-bioavailable, spectrum-selective Class I & IV HDAC inhibitor currently being studied in a Phase 2 trial as a combination therapy with durvalumab, targeting the programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) pathway, which has been implicated in advanced lung cancers. In preclinical models, mocetinostat with durvalumab demonstrated significant reduction in tumor volume compared to either agent alone.
About Durvalumab
Durvalumab is an investigational human monoclonal antibody directed against programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1). PD-L1 expression enables tumors to evade detection from the immune system through binding to PD-1 on cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Durvalumab blocks PD-L1 interaction with both PD-1 and CD80 on T cells, countering the tumour’s immune-evading tactics. Durvalumab is being developed alongside other immunotherapies to activate the patient’s immune system to attack the cancer. Durvalumab is being investigated in an extensive clinical trial programme, as monotherapy or in combination with tremelimumab, in NSCLC, bladder, head and neck, gastric, pancreatic, HCC and blood cancers. In 2015, durvalumab received Fast Track Designation for the treatment of patients with PD-L1–positive metastatic SCCHN, and in 2016, durvalumab was granted Breakthrough Designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a potential treatment for metastatic urothelial bladder cancer.
SOURCE: Mirati Therapeutics
Post Views: 203